Why Is Mexico’s Public Health System Betting Big on a Robot Named CyberKnife?
The IMSS officially confirmed the operational launch of a new CyberKnife radiosurgery robot in October 2025 at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI. This system is unique in Mexico's public sector.
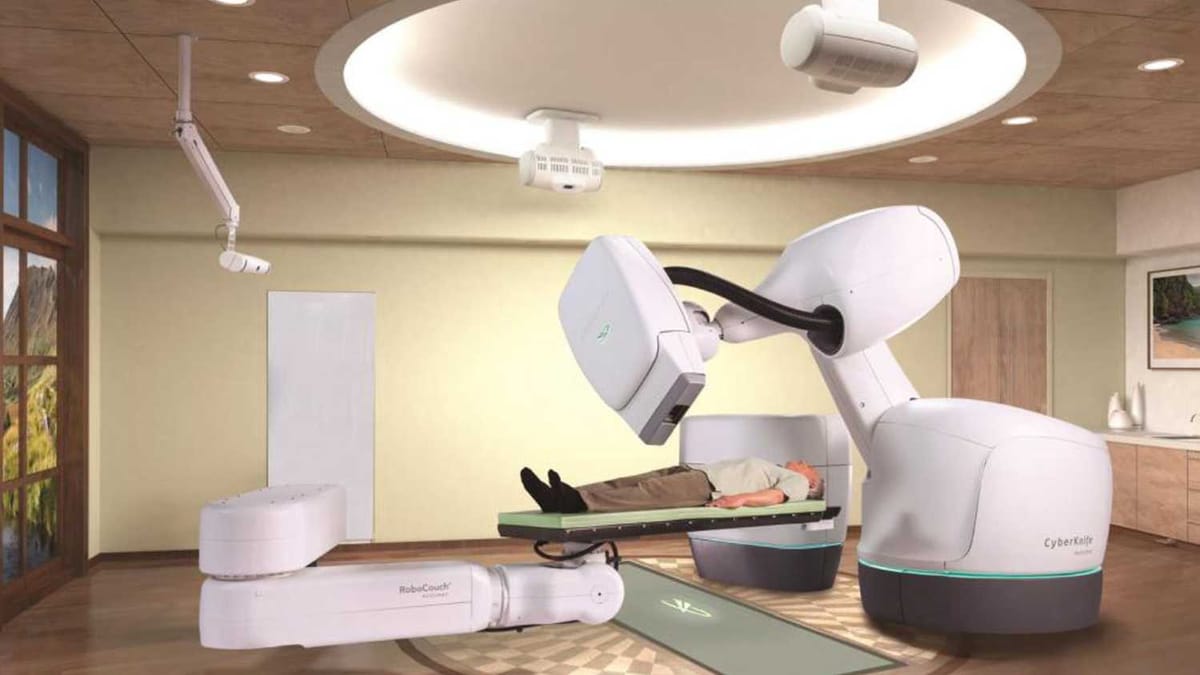
In a landmark development for Mexico's public healthcare sector, the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) officially confirmed the operational launch of a new CyberKnife radiosurgery robot in October 2025. The announcement was made by Zoé Robledo, the Director General of IMSS, during a high-profile visit to the Hospital de Oncología del Centro Médico Nacional (CMN) Siglo XXI . This event was not merely a technical upgrade but a strategic communication that framed the acquisition as a cornerstone of the institute's ongoing efforts to modernize and expand its oncology services. The presentation emphasized the integration of cutting-edge technology to improve patient outcomes and solidify the IMSS's position as a national leader in cancer treatment. The official press release highlighted that this technology, being the only one of its kind in the public sector, represents a major step forward in providing advanced, life-saving treatments to a wider segment of the Mexican population . The announcement was widely covered in national media, amplifying the message of the IMSS's commitment to technological advancement and transparency in the public health sector .
The strategic importance of this installation was further elaborated by the Director of the Hospital de Oncología, Dr. Rafael Medrano Guzmán, who noted that the new equipment is part of a comprehensive renovation of the hospital's operational areas, processes, and infrastructure . This modernization effort is designed to not only increase the hospital's productivity and the quality of care but also to incorporate sustainable technologies that reduce the institution's environmental footprint. The IMSS leadership has consistently framed this investment as a clear demonstration of its dedication to offering state-of-the-art treatments and comprehensive care to cancer patients across Mexico. The official statements from the IMSS leadership have repeatedly highlighted the CyberKnife as a unique and transformative technology that will significantly enhance the institute's capacity to treat complex oncological cases, thereby reinforcing its role as a national reference center for cancer care .

The CyberKnife radiosurgery robot was installed at the Hospital de Oncología del Centro Médico Nacional (CMN) Siglo XXI, a premier oncology hospital and a Unidad Médica de Alta Especialidad (UMAE) within the IMSS network . This location is strategically significant, as the hospital is a national reference center for cancer treatment and is already equipped with other advanced technologies, including two Da Vinci surgical robots . The choice of this hospital ensures that the sophisticated technology is placed within a facility that possesses the necessary infrastructure, a high volume of complex patient cases, and a team of specialized medical personnel to maximize its utility. The hospital's director, Dr. Rafael Medrano Guzmán, has emphasized that the institution is undergoing a complete renovation of its operational areas, processes, and equipment, making it the ideal setting for such an advanced system . The installation at this flagship institution also facilitates its use as a training hub for other hospitals within the IMSS system, further amplifying its impact on national cancer care standards.
The Hospital de Oncología at CMN Siglo XXI has a long-standing reputation for providing specialized cancer care and is equipped with other high-tech medical equipment, including nuclear medicine and advanced diagnostic imaging capabilities . The addition of the CyberKnife system complements its existing arsenal of treatment modalities. The hospital's infrastructure is being upgraded to be more sustainable, with improvements to electrical, hydraulic, and medical gas systems, ensuring that the new technology operates in a modern and efficient environment . This comprehensive approach to modernization, combining new equipment with facility upgrades, demonstrates a long-term vision for enhancing the quality and productivity of patient care. The hospital's role as a leader in the field is further solidified by this installation, which not only benefits its direct patients but also sets a new benchmark for oncology services across the country.

The CyberKnife system installed at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI is explicitly described as "unique in Mexico" by the IMSS, making it the only one of its kind in the entire country . This designation is a critical aspect of the announcement, as it underscores the pioneering role of IMSS in bringing this advanced technology to the public sector. While private hospitals in Mexico have previously acquired CyberKnife technology, the 2025 IMSS installation is the sole unit available to the millions of Mexicans who rely on the public health system . This distinction is crucial, as it highlights a significant step towards reducing health disparities and providing equitable access to advanced medical care. The uniqueness of this system within the public sector means that for many patients, the IMSS hospital in Mexico City is now the only accessible option for receiving this highly specialized form of radiosurgery.
This singularity within the public healthcare landscape means that the IMSS will be the primary provider of this specialized form of stereotactic radiosurgery for a vast patient population. This centralizes expertise and resources, which can be advantageous for ensuring high standards of care and operational efficiency. However, it also places a significant responsibility on the IMSS to manage the national demand for this treatment. The strategic decision to install the only public CyberKnife at the CMN Siglo XXI, a hospital already recognized for its expertise in complex oncology cases, is a logical step to ensure that the technology is utilized effectively . The system's uniqueness also makes the hospital a national and potentially international center of excellence for this type of treatment, attracting referrals and fostering research and development in the field of robotic radiosurgery.
The installation of the new CyberKnife system, in conjunction with two additional linear accelerators, is projected to triple the radiotherapy capacity at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI . This substantial increase in treatment capacity is a direct response to the growing demand for oncology services and the need to reduce waiting times for patients requiring radiation therapy. The ability to treat three times as many patients represents a transformative leap in the hospital's operational efficiency and its ability to provide timely care. This expansion is not merely an incremental improvement but a fundamental shift in the hospital's treatment throughput, which will have a significant positive impact on patient outcomes by allowing for earlier intervention. The projection of a threefold increase is a clear indicator of the high value placed on this technology by the IMSS administration, which sees it as a critical tool in the fight against cancer .
This projected increase in capacity is a key performance indicator for the success of the investment. The ability to triple the number of patients treated daily will alleviate the pressure on the hospital's existing radiotherapy services and reduce the backlog of patients waiting for treatment. This is particularly important for a public health system that serves a large and diverse population, where delays in treatment can have serious consequences for patient prognosis. The strategic planning behind this expansion is designed to optimize the use of the new equipment and ensure that the increased capacity is fully utilized. This focus on operational efficiency, combined with the advanced capabilities of the CyberKnife, will enable the hospital to deliver high-quality, precise treatments to a much larger number of patients, thereby significantly enhancing the overall effectiveness of the national cancer care program.

The projected tripling of radiotherapy capacity translates into a specific and measurable increase in the number of patients treated daily. The hospital's daily patient load for radiotherapy is expected to rise from 14 to 40 patients, a nearly threefold increase . This significant jump in daily throughput is a direct result of the advanced technology and efficiency of the new CyberKnife system and the two additional linear accelerators. The ability to treat 40 patients per day will dramatically reduce waiting lists and allow the hospital to manage its patient flow more effectively. This increase is not just about quantity but also about quality, as the CyberKnife's precision allows for shorter treatment sessions and fewer side effects, which can improve the overall patient experience and quality of life during treatment.
The increase from 14 to 40 daily patients is a testament to the technological superiority of the new equipment. The CyberKnife's robotic arm and real-time imaging capabilities allow for faster and more accurate treatment delivery compared to conventional radiotherapy systems. This efficiency, combined with the ability to treat multiple patients simultaneously on the different machines, is what enables such a dramatic increase in capacity. The hospital's ability to manage this increased workload will depend on a well-coordinated effort involving not only the medical physicists and radiation oncologists who operate the equipment but also the support staff who manage patient scheduling, preparation, and follow-up. The successful implementation of this expansion will serve as a model for other hospitals within the IMSS system and demonstrate the potential for technology to drive significant improvements in public healthcare delivery.
The installation of the CyberKnife system was part of a larger investment that also included two new linear accelerators at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI . This complementary installation is a crucial element of the overall strategy to enhance the hospital's radiotherapy capacity. While the CyberKnife is a highly specialized tool for stereotactic radiosurgery, the linear accelerators are the workhorses of conventional radiotherapy, used to treat a wider range of cancer types. By installing both types of equipment simultaneously, the IMSS is ensuring that the hospital has a comprehensive and versatile radiotherapy department capable of meeting the diverse needs of its patient population. The two new linear accelerators will allow the hospital to treat more patients with conventional radiotherapy, while the CyberKnife can be reserved for the most complex cases that require its unique precision.
The synergy between the CyberKnife and the linear accelerators is a key factor in the projected tripling of patient capacity. The new linear accelerators are state-of-the-art machines that offer advanced features such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) , which allow for more precise and effective treatments than older models . The combination of these advanced linear accelerators with the CyberKnife creates a powerful and flexible treatment platform that can be tailored to the specific needs of each patient. This integrated approach to radiotherapy, which leverages the strengths of different technologies, is a hallmark of modern cancer care and a clear indication of the IMSS's commitment to providing its patients with the best possible treatment options. The simultaneous installation of this equipment also allows for a more efficient use of resources, as the hospital can streamline its workflows and optimize its treatment planning and delivery processes.
Financial Investment and Cost Analysis
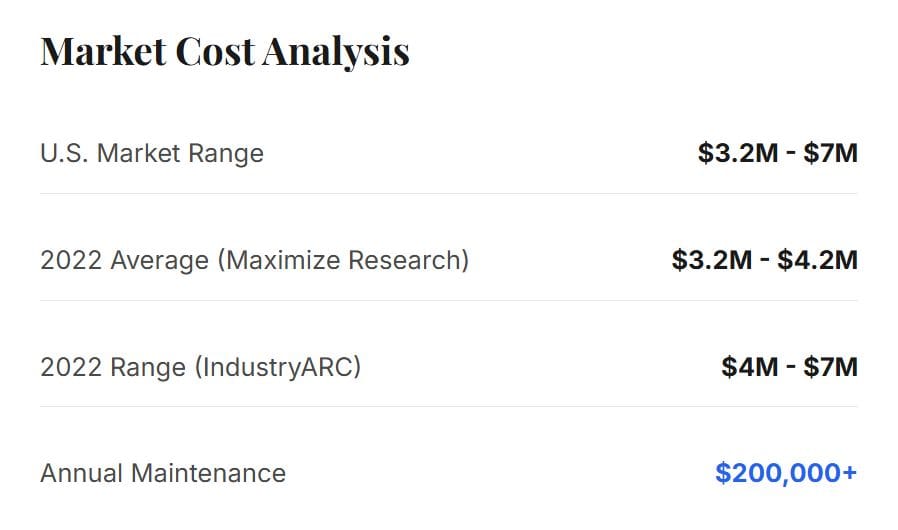
The acquisition cost of a CyberKnife radiosurgery robotic system in the United States is substantial, reflecting its advanced technology and precision. Market analysis indicates that the price for a single unit typically ranges from US $3.2 million to US $7 million . This wide range can be attributed to several factors, including the specific model, the inclusion of additional features and software packages, and the terms of the purchase agreement. For instance, a 2022 market report from Maximize Market Research placed the cost between US $3.2 million and US $4.2 million , while a 2022 report from IndustryARC estimated a higher range of US $4 million to US $7 million . This significant capital investment is a major consideration for any healthcare institution, particularly public health systems operating under tight budgetary constraints. The high cost is not limited to the initial purchase; annual maintenance contracts can exceed US $200,000, and the need for specialized personnel to operate the system adds to the ongoing operational expenses .
The high acquisition cost of the CyberKnife is a primary factor limiting its widespread adoption, especially in low- and middle-income countries . The financial barrier is significant, as it requires a long-term commitment of capital and resources. The cost of the equipment is just one component of the total investment; hospitals must also consider the cost of facility modifications, staff training, and the development of specialized treatment planning and quality assurance programs. The high price tag is justified by the system's unique capabilities, which include frameless stereotactic radiosurgery, real-time tumor tracking, and sub-millimeter accuracy. These features allow for the treatment of tumors in difficult-to-reach locations and can lead to better patient outcomes with fewer side effects. However, the economic reality of such a large investment means that the decision to acquire a CyberKnife is a strategic one that must be carefully weighed against other pressing healthcare needs.

The cost of CyberKnife treatment varies significantly across different countries, reflecting differences in healthcare systems, economic conditions, and market dynamics. According to data from Bookimed, a medical tourism platform, the average cost of CyberKnife treatment is around $10,600 . However, this figure can be misleading, as the cost can range from as low as $4,750 in Turkey to as high as $45,000 in the United States . This wide variation in cost is a reflection of the different factors that influence the price of medical care in each country. In countries with a high cost of living, such as the United States and Germany, the cost of CyberKnife treatment is naturally higher. In countries with a lower cost of living, such as Turkey and India, the cost of treatment is more affordable.
The cost of CyberKnife treatment is also influenced by the level of competition in the market. In countries with a large number of CyberKnife centers, such as Turkey, the cost of treatment is generally lower due to increased competition . In countries with fewer CyberKnife centers, the cost of treatment is often higher due to a lack of competition. The cost of CyberKnife treatment is also affected by the level of government regulation in the healthcare sector. In countries with a strong public healthcare system, such as the United Kingdom, the cost of CyberKnife treatment is often covered by the government. In countries with a more privatized healthcare system, such as the United States, the cost of treatment is often borne by the patient or their insurance company.
The first CyberKnife system installed at the IMSS in 2012 represented a significant financial commitment by the institution. According to a report from La Jornada, the cost of this system was approximately 80 million pesos . At the time, this was equivalent to around $4 million USD, a figure that is consistent with the general market cost of this technology . This investment was a major step forward for the IMSS, as it provided the institution with the ability to offer a new and innovative treatment option to its patients. The 2012 installation was also a significant event for the Mexican healthcare system as a whole, as it marked the first time that a public institution in the country had acquired such an advanced piece of medical equipment. The cost of the 2012 installation was a reflection of the high value that the IMSS placed on providing its patients with the best possible care.
The 80 million peso investment in the 2012 CyberKnife system was a major undertaking for the IMSS, and it required careful planning and budgeting. The institution had to secure the necessary funding, as well as the physical space and the trained personnel to operate the system. The investment also included the cost of training the medical staff, as well as the ongoing costs of maintenance and support. The 2012 installation was a testament to the IMSS's commitment to innovation and its willingness to invest in new technologies that could improve the lives of its patients. The cost of the 2012 installation was also a reflection of the growing demand for advanced cancer treatments in Mexico. The IMSS recognized that it needed to keep pace with the latest developments in medical technology in order to meet the needs of its patient population.

While the specific cost of the 2025 CyberKnife installation has not been publicly disclosed, it is likely to be significantly higher than the 80 million pesos that was paid for the original system in 2012. This is due to a number of factors, including inflation, the increased complexity of the newer systems, and the additional costs associated with installation and commissioning. The newer CyberKnife systems are more advanced than the original system, with improved imaging capabilities, more precise targeting, and a wider range of treatment options. These improvements come at a cost, and it is likely that the IMSS has had to pay a premium for the latest technology. In addition to the cost of the equipment itself, there are also the costs of training staff, developing new treatment protocols, and integrating the new system into the hospital's existing infrastructure.
Despite the higher cost, the 2025 investment is a clear indication of the IMSS's continued commitment to providing its patients with the most advanced cancer treatments available. The new CyberKnife system is expected to provide even better outcomes for patients than the original system, and it will also allow the hospital to treat a wider range of cancers. The investment in the new CyberKnife system is also a reflection of the growing demand for this type of treatment in Mexico, as more and more patients are seeking out non-invasive and highly precise forms of cancer therapy. The IMSS's decision to invest in a new CyberKnife system is a strategic one, and it is expected to have a major impact on the future of cancer care in Mexico. The institution's willingness to make this significant financial commitment is a testament to its belief in the power of technology to improve the lives of its patients.
In addition to the CyberKnife system, the IMSS has also invested in two new linear accelerators (linacs) for the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI . The cost of these new linacs has not been publicly disclosed, but it is likely to be a significant amount, as these are highly complex and expensive pieces of medical equipment. The cost of a new linear accelerator can vary depending on the specific model and the features that are included, but it is typically in the range of several million dollars. The IMSS has recently approved the replacement of 12 additional linacs at other hospitals across the country, at a total cost of over 2.4 billion Mexican pesos . This gives some indication of the scale of the investment that the IMSS is making in this technology.
The investment in new linear accelerators is a critical component of the IMSS's strategy to modernize its radiotherapy services and to improve the quality of care for its patients. The new linacs are more advanced and efficient than the older machines they are replacing, and they will allow the hospital to offer a wider range of treatment options. The new linacs will also help to reduce waiting times and to improve the overall efficiency of the radiotherapy department. The investment in new linear accelerators is a clear indication of the IMSS's commitment to providing its patients with the most advanced and effective cancer treatments available. The institution's willingness to make this significant financial commitment is a testament to its belief in the power of technology to improve the lives of its patients.
The total investment by the IMSS in radiotherapy infrastructure in recent years has been substantial. In addition to the cost of the new CyberKnife system and the two new linear accelerators at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI, the IMSS has also approved the replacement of 12 additional linacs at other hospitals across the country, at a total cost of over 2.4 billion Mexican pesos . This comprehensive modernization program is a clear indication of the IMSS's commitment to providing its patients with the most advanced and effective cancer treatments available. The total investment in radiotherapy infrastructure is a reflection of the growing demand for this type of treatment in Mexico, as more and more patients are seeking out non-invasive and highly precise forms of cancer therapy.
The IMSS's investment in radiotherapy infrastructure is also a strategic one, as it is designed to position the institution as a leader in cancer care in Mexico and in Latin America. The new equipment will not only improve the quality of care for IMSS beneficiaries but will also allow the institution to attract patients from other countries in the region. The investment in radiotherapy infrastructure is also expected to have a positive impact on the Mexican economy, as it will create jobs and stimulate the growth of the domestic medical technology industry. The IMSS's long-term commitment to investing in radiotherapy infrastructure is a clear indication of its belief in the power of technology to improve the lives of its patients and to strengthen the Mexican healthcare system as a whole.

History and Previous Installations
The first CyberKnife system in Mexico was installed at the Hospital de Oncología del Centro Médico Nacional Siglo XXI in 2012 . This installation was a major milestone for the IMSS and for the Mexican healthcare system as a whole. The system was a state-of-the-art piece of medical equipment that provided a new and innovative treatment option for cancer patients. The 2012 installation was the result of a major investment by the IMSS, which recognized the potential of the CyberKnife system to improve the lives of its patients. The system was installed in a dedicated room at the hospital, and it was operated by a team of highly trained medical professionals. The 2012 installation was a major undertaking, and it required careful planning and coordination to ensure that the system was installed and commissioned successfully.
The 2012 CyberKnife system was a significant upgrade over the existing radiotherapy equipment at the hospital. The system was equipped with a robotic arm that allowed for a high degree of precision in the delivery of radiation. The system also had a sophisticated image guidance system that allowed the medical team to track the tumor in real-time and to adjust the radiation beam accordingly. The 2012 installation was a major step forward for the IMSS, and it helped to establish the institution as a leader in cancer care in Mexico. The system was used to treat a wide range of cancers, including brain tumors, lung cancer, and prostate cancer. The 2012 installation was a major success, and it helped to improve the quality of life for thousands of patients.
The 2012 installation of the CyberKnife system at the IMSS was not just a significant event for Mexico; it was also a major milestone for the entire Latin American region. At the time of its installation, the IMSS was the only public institution in Latin America to have a CyberKnife system . This made the IMSS a regional leader in the field of radiosurgery, and it helped to raise the profile of the institution on the international stage. The 2012 installation was a major source of pride for the IMSS and for the Mexican people, as it demonstrated the country's commitment to providing its citizens with the best possible healthcare. The 2012 installation was also a major event for the Latin American medical community, as it provided a new opportunity for training and research.
The 2012 installation of the CyberKnife system at the IMSS had a profound impact on the development of radiosurgery in Latin America. The system was used to train a new generation of medical professionals in the use of advanced radiosurgery techniques. The system was also used to conduct research on the effectiveness of the CyberKnife system in treating a wide range of cancers. The 2012 installation was a major catalyst for the development of a regional network of radiosurgery centers. The IMSS played a key role in this process, by sharing its expertise and by providing training and support to other institutions in the region. The 2012 installation was a major step forward for the IMSS, and it helped to establish the institution as a regional hub for cancer care.
The cost of CyberKnife treatment in the private sector in Mexico is significantly higher than in the public sector. According to a 2012 report, a single session of CyberKnife treatment in a private hospital could cost between 150,000 and 500,000 pesos . This is a substantial amount of money, and it is well beyond the reach of most Mexican citizens. The high cost of CyberKnife treatment in the private sector is a reflection of the high cost of the technology, as well as the high overhead costs of private hospitals. The high cost of treatment is a major barrier to access for many patients, and it is one of the main reasons why the IMSS's acquisition of a CyberKnife system was so significant.
The high cost of CyberKnife treatment in the private sector is also a reflection of the lack of competition in the market. At the time of the 2012 report, there was only one private hospital in Mexico that offered CyberKnife treatment . This lack of competition allowed the hospital to charge a premium for its services. The high cost of treatment is also a reflection of the high demand for the service. Many patients are willing to pay a high price for CyberKnife treatment, as it is a non-invasive alternative to surgery. The high cost of treatment is a major challenge for the Mexican healthcare system, and it is one of the main reasons why the IMSS's investment in a CyberKnife system was so important.
The acquisition of the new CyberKnife system in 2025 is the latest in a series of significant investments by the IMSS to modernize its radiotherapy infrastructure. The institution has been engaged in a comprehensive program to upgrade its equipment and facilities, ensuring that its beneficiaries have access to the latest and most effective cancer treatments. This modernization effort has included the replacement of aging linear accelerators, the installation of new treatment planning systems, and the renovation of treatment rooms. The IMSS has also invested heavily in the training of its medical and technical staff, ensuring that they have the skills and expertise to operate the new equipment effectively. This commitment to continuous improvement has positioned the IMSS as a leader in cancer care in Latin America.
The modernization efforts at the IMSS are not just about acquiring new technology; they are also about improving the overall quality and efficiency of patient care. The new equipment is more precise and faster than the older machines it is replacing, which means that patients can receive more effective treatment with fewer side effects. The new equipment is also more reliable, which helps to reduce downtime and improve the overall efficiency of the radiotherapy department. The IMSS has also implemented new workflows and processes to optimize the use of the new equipment and to ensure that patients are treated in a timely and efficient manner. This comprehensive approach to modernization has resulted in a significant improvement in the quality of care for IMSS beneficiaries.
The 2025 installation of the CyberKnife system at the IMSS is a major milestone in the evolution of national healthcare in Mexico. The acquisition of this advanced technology is a clear indication of the government's commitment to providing its citizens with access to the best possible medical care. The installation of the CyberKnife system is also a major step forward in the fight against cancer in Mexico, as it will allow the IMSS to treat a wider range of cancers with greater precision and fewer side effects. The installation of the CyberKnife system is also expected to have a positive impact on the Mexican economy, as it will create jobs and stimulate the growth of the domestic medical technology industry.
The 2025 installation of the CyberKnife system is also a major step forward in the development of a more equitable healthcare system in Mexico. By providing this advanced treatment in the public sector, the IMSS is helping to make it more affordable and accessible to all Mexican citizens, regardless of their socioeconomic status. This is a major step forward in the fight against health disparities in the country, and it is a clear indication of the government's commitment to social justice. The 2025 installation of the CyberKnife system is a major achievement for the IMSS and for the Mexican people, and it is a sign of a brighter future for healthcare in the country.
Technical and Operational Details
The CyberKnife radiosurgery system is manufactured by Accuray Incorporated, a leading radiation oncology company based in Sunnyvale, California . The system is a state-of-the-art piece of medical equipment that is designed to deliver highly targeted doses of radiation to tumors anywhere in the body. The CyberKnife system is a non-invasive alternative to surgery, and it is used to treat a wide range of cancers, including brain tumors, lung cancer, and prostate cancer. The system is equipped with a robotic arm that allows for a high degree of precision in the delivery of radiation. The system also has a sophisticated image guidance system that allows the medical team to track the tumor in real-time and to adjust the radiation beam accordingly.
The CyberKnife system is a complex piece of equipment that is made up of a number of different components. The main components of the system are the robotic arm, the linear accelerator, and the image guidance system. The robotic arm is a highly maneuverable device that can move the linear accelerator to any position around the patient. The linear accelerator is the device that produces the high-energy radiation that is used to treat the tumor. The image guidance system is a sophisticated imaging system that allows the medical team to see the tumor in real-time and to track its movement. The CyberKnife system is a highly integrated system that is designed to work together to deliver a precise and effective treatment.
The CyberKnife system is a versatile tool that is used to treat a wide range of cancers and other medical conditions. The system is particularly well-suited for the treatment of tumors that are located in difficult-to-reach areas of the body, such as the brain and spine. The system's high degree of precision allows the medical team to deliver a high dose of radiation to the tumor while minimizing the dose to the surrounding healthy tissue. This is a major advantage over traditional radiotherapy methods, which can often cause significant damage to healthy tissue. The CyberKnife system is also used to treat a number of non-cancerous conditions, such as trigeminal neuralgia and arteriovenous malformations.
The CyberKnife system is a non-invasive treatment option, which means that it does not require any incisions or anesthesia. This is a major advantage for patients, as it means that they can avoid the risks and complications of surgery. The CyberKnife system is also a painless treatment option, and most patients are able to return to their normal activities immediately after the treatment. The CyberKnife system is a convenient treatment option, as it typically requires only one to five treatment sessions. This is a major advantage over traditional radiotherapy methods, which can often require daily treatments for several weeks. The CyberKnife system is a safe and effective treatment option for a wide range of cancers and other medical conditions, and it is a valuable tool in the fight against these devastating diseases.
The integration of the new CyberKnife system with the two new linear accelerators at the Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI creates a powerful synergy that enhances the hospital's overall radiotherapy capabilities. While the CyberKnife is a highly specialized tool for stereotactic radiosurgery, the linear accelerators are the workhorses of conventional radiotherapy. This combination allows the hospital to offer a comprehensive and tiered approach to radiation therapy, matching the right technology to the specific needs of each patient. The CyberKnife can be reserved for the most complex cases that require its unique precision, while the linear accelerators can be used for more routine treatments. This integrated approach is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and resource utilization.
The synergy between the CyberKnife and the linear accelerators is a key factor in the projected tripling of patient capacity. The new linear accelerators are state-of-the-art machines that offer advanced features such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), which allow for more precise and effective treatments than older models . The combination of these advanced linear accelerators with the CyberKnife creates a powerful and flexible treatment platform that can be tailored to the specific needs of each patient. This integrated approach to radiotherapy, which leverages the strengths of different technologies, is a hallmark of modern cancer care and a clear indication of the IMSS's commitment to providing its patients with the best possible treatment options.
The installation of the new CyberKnife system is a major step forward in the IMSS's efforts to provide comprehensive cancer care to its beneficiaries. The system is a valuable addition to the hospital's existing arsenal of treatment modalities, which includes surgery, chemotherapy, and conventional radiotherapy. The CyberKnife's ability to treat tumors with sub-millimeter accuracy makes it an ideal tool for treating complex cases that are not suitable for surgery or conventional radiotherapy. The system's non-invasive nature also makes it a more attractive option for patients who are not good candidates for surgery.
The integration of the CyberKnife system into the hospital's existing infrastructure is also expected to have a positive impact on the quality of care for all cancer patients. The system's advanced imaging capabilities will allow for more accurate diagnosis and staging of tumors, which will lead to more effective treatment planning. The system's ability to deliver highly targeted doses of radiation will also help to reduce the side effects of treatment, which will improve the quality of life for patients. The installation of the CyberKnife system is a clear indication of the IMSS's commitment to providing its patients with the most advanced and effective cancer treatments available.
References
[151] Tintapublicanoticias.com - Hospital de Oncología del CMN Siglo XXI fortalece su infraestructura con tecnología de punta. Link[163] La Jornada - Cost analysis of CyberKnife installation (2012). Link[166] Gob.mx - IMSS Council approves replacement of 12 linear accelerators. Link[192] PR Newswire - First CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System Goes Live in Mexico. Link[199] Bookimed - CyberKnife treatment cost comparison across countries. Link[225] Imagen Radio - Un paso a la victoria sobre el cáncer: IMSS pone en marcha el CyberKnife. Link[226] IMSS Official Archive - CyberKnife installation announcement. Link




